Both vitamin deficiencies (much lower amounts than our bodies need) and excess (higher than the maximum our bodies need/tolerate) may lead to adverse symptoms for some vitamins. For example, vitamin A deficiency may result in night blindness first leading to blindness later on, and tissues like eyes and skin may become dry and damaged while infections are more likely due to the immune system not working properly especially in infants and children, whose growth and development may be slowed. However this deficiency can be reversed by taking high vitamin A doses for several days. On the other hand, excess vitamin A may result in hair loss, cracked lips, dry skin, weakened bones, headaches, and increased pressure in the brain, although these effects requires intake of really high doses and are reversed by stopping vitamin A intake.

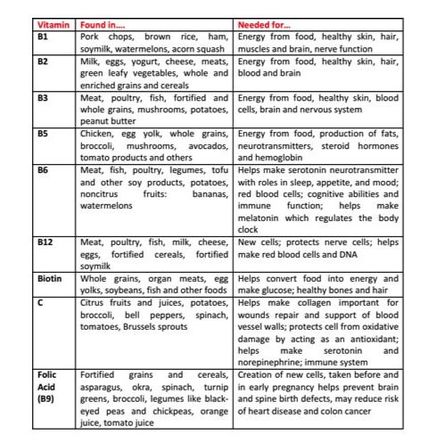
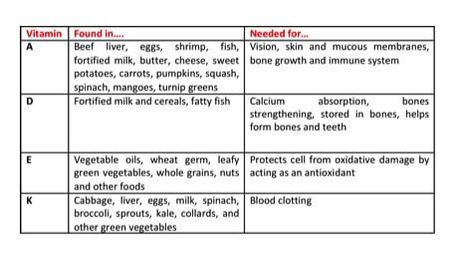
There are a total of 13 vitamins, which can be divided in two groups: those soluble in water, and those soluble in fat. All B vitamins and vitamin C are water-soluble and our bodies can’t store them. They leave us quickly via our kidneys and then in our urine, so we need to provide our bodies with them often, ideally every day. In contrast, vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble, absorbed in our intestines in fatty forms and easily stored in our bodies in the liver and fatty tissues for long periods of time (except vitamin K). This is why toxicity may occur if too much is taken of a fat-soluble vitamin, especially vitamin A or D.
All vitamins are absorbed in the small intestine, and then transported to specific tissues in the bloodstream; fat-soluble vitamins need to be transported first by the lymphatic system after intestinal absorption to the blood. At the right destination, vitamins help "reactions" occur, several carried out by enzymes that need a little help from "coenzymes" which some of these vitamins act as. Vitamins C and E are well known as "antioxidants", meaning they protect our cells from excessive accumulation of "free radicals" that may cause "oxidative stress" and result in an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, cancer and other diseases.
For a fun and informative 5min TED Ed video on how we absorb vitamins, how they are transported and what they help us with, watch: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ISZLTJH5lYg
Water Soluble Vitamins



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed